Aluminum PCB Guide
Aluminum PCBs help keep electronic devices cool. You see them where heat control is very important. These boards have a metal base. The base moves heat away from important parts. Aluminum PCBs are helpful if you use:
Industrial laser systems
Automation equipment
Aerospace and defense electronics
Test and measurement gear
You get better reliability and performance in tough places.
Key Takeaways
Aluminum PCBs spread heat very well. This makes them great for high-power uses like LED lights and power electronics. These boards last longer than regular PCBs. They do not bend or break easily from heat, shaking, or bumps. Pick the right aluminum PCB for your project. Use single-layer for simple circuits. Use double-layer for more complex ones. Use multilayer for advanced designs. Add a solder mask and silkscreen layers to protect the board. These layers also help with clear labels for easy building and fixing. Think about the thickness of the dielectric layer. Thin layers move heat better. Thick layers keep electricity from leaking. Aluminum PCBs save money for tough jobs. They work well in cars and factories. Always use good materials and careful making steps. This helps your aluminum PCBs last longer and work better. Talk to PCB makers to pick the best design and materials. This will help your project work its best.
Aluminum PCBs Overview
Definition
Aluminum PCBs are used in many things that need cooling. These boards have a metal base that pulls heat away from key parts. They have three main layers: thick copper foil, a special dielectric layer, and an aluminum base. This makes the board handle heat better than regular PCBs. Aluminum PCBs are good for high-power electronics, LED lights, and motor drives. They are used where heat might hurt circuits or make them work worse.
Key Features
Aluminum PCBs are strong and manage heat very well. The copper layer is thick and can carry more current. The dielectric layer moves heat fast. The aluminum base makes the board strong and helps cool it down. Some boards have a special membrane for extra safety. Here is a table that lists the main materials in aluminum PCBs:
Layer Type | Description |
|---|---|
Copper Foil Layer | Thicker than normal CCLs (1oz-10oz) for higher current carrying capacity. |
Dielectric Layer | Thermally conductive, 50μm to 200μm thick, with low thermal resistance. |
Aluminum Base | Made of aluminum substrate, providing high thermal conductivity. |
Aluminum Base Membrane | Protective layer for the aluminum surface, available in two types based on temperature tolerance. |
These boards stay steady even when it gets hot or cold. They have much lower thermal resistance than other PCBs. You can use them in hard places and not worry about them failing.
Comparison with FR-4
You might ask how aluminum PCBs are different from FR-4 boards. FR-4 boards use fiberglass and epoxy, which do not move heat well. Aluminum PCBs have much lower thermal resistance. They cool better and do not change size as much when hot. Here is a table that shows how they are different:
Characteristic | Aluminum PCBs | FR-4 PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Copper Foil Layer | Thicker (1oz-10oz) for higher capacity | Thinner than aluminum PCBs |
Dielectric Layer | Thermally conductive, low thermal resistance | Less effective |
Aluminum Base | High thermal conductivity | Not aluminum |
Thermal Resistance | 20-22 degrees per watt | |
Dimensional Stability | 2.5%-3.0% size change from 30-140°C | Higher size change under heat |
Thermal Expansion Coefficient | Close to copper (22ppm/C) | Varies, can lead to issues |
Reliability | Extremely reliable | Less reliable |
Applications | General applications |
Tip: If you need a board for high-power or hot places, pick aluminum PCBs. They work better and last longer in your devices.
Structure
Copper Layer
You find the copper layer at the top of the board. This layer carries electrical signals and power between components. The copper layer in aluminum PCBs is thicker than in standard boards. Thicker copper lets you move more current and helps with heat transfer. You can choose different copper weights based on your needs. Here is a table that shows the typical thickness range for copper layers:
Copper Weight | Thickness (mil) | Thickness (microns) |
|---|---|---|
0.5 oz/sq ft | 0.671 | 17.05 |
1.0 oz/sq ft | 1.34 | 34.1 |
2.0 oz/sq ft | 2.68 | 68.1 |
3.0 oz/sq ft | 4.02 | 102.2 |
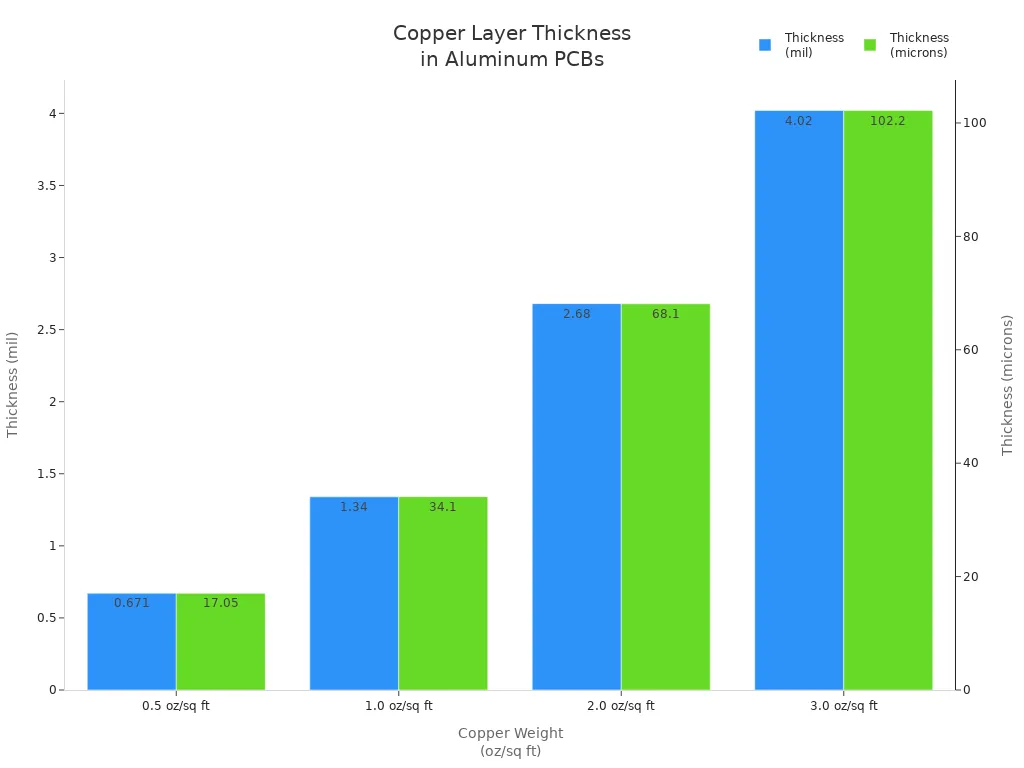
You see that higher copper weights give you thicker layers. Thicker copper helps your board handle more power and heat. You get better performance in high-current circuits.
Dielectric Layer
The dielectric layer sits between the copper and the aluminum base. This layer insulates the copper from the metal base. It also moves heat from the copper to the aluminum. You need a dielectric that has high thermal conductivity and low electrical conductivity. Most boards use a special resin or polymer for this layer. The thickness of the dielectric layer affects how well your board cools down. Thin layers move heat faster, but thick layers give you more insulation. You must balance these features for your design.
Aluminum Base
The aluminum base forms the foundation of the board. This layer gives your board strength and stability. Aluminum conducts heat very well. It pulls heat away from the copper and dielectric layers. You get better cooling for your components. The aluminum base also makes your board tough. It resists bending and damage. You can use aluminum PCBs in places with vibration or shock. Some boards use a copper clad laminate (CCL) to improve performance. You may see resin-insulated through-holes in the base. These holes let you mount components and keep them safe from electrical shorts.
Tip: Choose the right thickness for each layer to get the best mix of cooling, strength, and electrical performance.
Solder Mask & Silkscreen
The solder mask and silkscreen layers help protect and label your aluminum PCB. These layers go on top of the copper traces. They are important for how the board works and looks.
Solder Mask
The solder mask covers the copper traces on your aluminum PCB. This layer acts like a shield. It keeps the copper safe from air, water, and dirt. The solder mask also stops solder from making unwanted bridges during assembly. This means you get fewer short circuits and your board works better.
Most solder masks are made from green epoxy resin. You can also pick white, black, red, or blue. The color does not change how the board works. It can help you see problems or match your brand.
Here are some main reasons to use a solder mask on your aluminum PCB:
Prevents short circuits by stopping solder from spreading.
Protects copper from rust and damage from the environment.
Improves appearance and makes it easier to check the board.
Enhances durability so the board lasts longer in tough places.
Tip: If you use LED lights, a white solder mask is good. It reflects more light and helps keep your board cool.
Silkscreen
The silkscreen layer puts words and symbols on your aluminum PCB. You use this layer to print names, numbers, and logos. The silkscreen helps you find parts, pin numbers, and test spots.
Most silkscreen is white, but you can use other colors. The ink must stand up to heat and chemicals when you build the board. Good silkscreen printing makes building and fixing the board much easier.
Here is a table that shows how solder mask and silkscreen are different:
Layer | Main Function | Typical Material | Common Color |
|---|---|---|---|
Solder Mask | Protects copper, prevents shorts | Epoxy resin | Green |
Silkscreen | Adds labels and markings | Heat-resistant ink | White |
Why These Layers Matter
You need both solder mask and silkscreen for a strong aluminum PCB. The solder mask keeps your board safe and working well. The silkscreen gives you clear labels for building and fixing. Always add these layers when you design your aluminum PCB for the best results.
Note: Good solder mask and silkscreen help your aluminum PCB work better and last longer, even in hard places.
Advantages
Heat Dissipation
You need your electronic devices to stay cool, especially when they handle a lot of power. Aluminum PCBs help you manage heat much better than standard boards. The metal base pulls heat away from important parts fast. This keeps your circuits safe and working well. When you use high-power LEDs or power converters, heat can build up quickly. If you do not remove this heat, your components can fail.
Aluminum PCBs have excellent thermal conductivity. This means they move heat away from hot spots and spread it across the board. You lower the risk of damage to your circuits. You also get longer life from your devices. Many engineers choose aluminum PCBs for high-density circuits and power electronics because they keep things cool and stable.
Did you know? Aluminum PCBs can handle heat so well that they are the top choice for LED lighting and power supplies. You get better performance and fewer failures.
Durability
You want your boards to last, even when they face tough conditions. Aluminum PCBs give you strong durability. They stand up to heat, vibration, and shock better than many other types of boards. The metal base makes the board less likely to bend or break.
Aluminum PCBs have a thermal conductivity about 600 times greater than FR-4 boards. This lets them get rid of heat quickly, which is important in high-heat jobs.
The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) for FR-4 is much higher than copper. This can cause problems when the board heats up and cools down. You might see cracks or layers coming apart.
Aluminum’s CTE is close to copper’s. This match means less stress on the board during heating and cooling. You see fewer failures like delamination or broken traces.
You can trust aluminum PCBs to work well in places where temperature changes a lot. They keep their shape and keep working, even after many heating and cooling cycles.
Packing Density
You often need to fit more circuits into a small space. Aluminum PCBs let you do this safely. Because they move heat away so well, you can place components closer together. You do not have to worry as much about overheating.
Here is a table that shows why packing density matters:
Feature | Benefit for You |
|---|---|
High heat dissipation | Place parts closer together |
Strong base | Supports more components |
Stable performance | Less risk of overheating |
You can design smaller, lighter devices without giving up power or reliability. This makes aluminum PCBs a smart choice for modern electronics where space is tight.
Reliability
You want your devices to work every time you use them. This is very important if you use them for a long time or in hard places. Aluminum PCBs help make your devices more reliable. They stop many problems that can break normal boards.
Aluminum PCBs can handle heat, water, and shaking. The metal base keeps the board flat and strong. You do not need to worry about the layers coming apart. The board stays together, even if you drop it or use it in machines that move.
Here are some reasons why aluminum PCBs are so reliable:
Thermal Stability: The aluminum base moves heat away fast. This keeps your parts cool and helps them last longer. You will see fewer problems from too much heat.
Mechanical Strength: The metal core makes the board very tough. It does not bend or snap easily. You can use it in cars, factories, or outside.
Moisture Resistance: Aluminum PCBs do not soak up water like some other boards. This stops short circuits and rust.
Consistent Performance: The board keeps working, even when it gets hot or cold. You get steady results in all kinds of weather.
Note: If you need a board for LED lights, power supplies, or car electronics, aluminum PCBs are a great choice.
You can see the benefits in this table:
Feature | Aluminum PCB Reliability Benefit |
|---|---|
Heat Resistance | Prevents thermal damage |
Strong Structure | Reduces risk of cracks or breaks |
Moisture Protection | Stops corrosion and short circuits |
Stable Performance | Works well in changing temperatures |
You will fix your boards less often. This saves you money and time. When you use aluminum PCBs, your devices keep working.
Many companies use aluminum PCBs for important jobs. You find them in medical tools, street lights, and power units. These boards keep working when others might stop.
If you want a board that lasts, pick aluminum PCBs. You will worry less and your projects will work better.
Tip: Always check that your aluminum PCB supplier uses good materials. Careful work makes your board even more reliable.
Types of Aluminum PCBs
Single-Layer
Single-layer aluminum PCBs are good for simple jobs. They have one copper layer on top. Under the copper is a dielectric and an aluminum base. You use these boards for basic circuits. They do not need tricky designs. The board is easy to make. It handles heat well and is strong.
Single-layer aluminum PCBs work in LED lights, power modules, and car sensors. You can put parts on them easily. The aluminum base moves heat away fast. This stops parts from getting too hot. You see fewer problems from overheating. If you want a board that works well for high-power jobs, single-layer aluminum PCBs are a smart pick.
Key benefits of single-layer aluminum PCBs:
Simple design makes them easy to build
Cost is lower than boards with more layers
Moves heat away well in basic circuits
Tough and strong for hard places
Tip: Use single-layer aluminum PCBs for LED strips and power converters. They last a long time and work well.
Double-Layer
Double-layer aluminum PCBs are for harder circuits. These boards have two copper layers. A dielectric sits between the copper layers. The aluminum base is at the bottom. You can send signals on both sides. This gives you more ways to design your board.
Double-layer aluminum PCBs let you put more parts on the board. You do not lose good heat control. The extra copper helps with power and signals. You find double-layer aluminum PCBs in factory controls, car electronics, and advanced LED drivers.
Advantages of double-layer aluminum PCBs:
More ways to connect parts in tough circuits
Can fit more parts for advanced designs
Two copper layers help move heat better
Good for surface-mount and through-hole parts
You get a mix of good price and strong performance. Double-layer aluminum PCBs help you make devices with more features.
Multilayer
Multilayer aluminum PCBs are for the hardest jobs. These boards have three or more copper layers. Dielectric materials go between the layers. The aluminum base holds everything together. You can send many signals and power lines. Multilayer aluminum PCBs handle fast circuits and big power loads.
You use multilayer aluminum PCBs in phones, power supplies, and medical tools. Extra layers keep power and signals apart. This lowers noise and makes the board work better. The aluminum base keeps the board cool, even with lots of parts.
Why pick multilayer aluminum PCBs?
Good for hard and packed circuits
Better heat control for strong devices
Less electrical noise and better signals
Strong support for heavy parts
Type | Layers | Typical Use Cases | Thermal Performance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Single-Layer | 1 | LED strips, power modules | Good | Low |
Double-Layer | 2 | Industrial controls, automotive | Better | Medium |
Multilayer | 3+ | Telecom, medical, power supplies | Best | Higher |
Note: Multilayer aluminum PCBs give you top performance for hard and powerful electronics. They work well and keep cool.
Pick the right aluminum PCB type for your project. You get better results when you choose the best board for your needs.
Flexible
Flexible aluminum PCBs let you make new kinds of devices. These boards can bend and twist but do not break. You use them where space is small or the board must move. Flexible aluminum PCBs have metal core PCB benefits and can flex.
You see flexible aluminum PCBs in LED strips and wearables. They are also in car lights. These boards help you make shapes that stiff boards cannot do. You can wrap them around corners or fit them in curved spots. This helps you make cool and useful designs.
Key features of flexible aluminum PCBs:
Thin and light design
Moves heat well for better cooling
Can bend, fold, or twist without breaking
Stays strong against shaking and bumps
Tip: If your device moves or has a special shape, use a flexible aluminum PCB. You get both bending and good heat control.
Flexible aluminum PCBs have a thin aluminum base. They use a special flexible dielectric layer. The copper layer is on top like other aluminum PCBs. The flexible dielectric lets the board bend and still move heat away. You use these boards where regular PCBs would crack or break.
Here is a table that shows how flexible aluminum PCBs are different from rigid aluminum PCBs:
Feature | Flexible Aluminum PCB | Rigid Aluminum PCB |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Can bend and twist | Stays flat |
Thermal Management | Excellent | Excellent |
Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
Common Uses | Wearables, LEDs | Power supplies |
You can solder parts onto flexible aluminum PCBs like on stiff boards. The flexible design does not make the board weak or lose heat control. You get the same strong board with more ways to design.
Flexible aluminum PCBs help you fix problems in new electronics. You can make things smaller, lighter, and tougher. These boards work well in products that move or need to fit in odd places.
Note: Always check how much you bend flexible aluminum PCBs. If you bend too much, you can hurt the board or the parts.
Hybrid
Hybrid aluminum PCBs give you two kinds of features. You mix different materials to get what you want. Most hybrid aluminum PCBs use an aluminum base and other circuit layers like FR-4 or flexible polyimide. This mix helps you balance price, strength, and cooling.
You use a hybrid aluminum PCB when you need good cooling in one spot and normal circuits in another. For example, you put power parts on the aluminum side and signal parts on the FR-4 side. This way you save money and space.
Benefits of hybrid aluminum PCBs:
Custom cooling for different board parts
Costs less than full aluminum multilayer boards
More ways to design hard circuits
Good for mixed-signal and power jobs
You see hybrid aluminum PCBs in power supplies and car control units. They are also in LED drivers. These boards help you handle high power and sensitive signals on one board.
Here are some common hybrid aluminum PCB types:
Aluminum base with FR-4 layers on top
Aluminum base with flexible polyimide layers
Aluminum base with both stiff and flexible parts
Tip: Use hybrid aluminum PCBs when you need strong cooling and advanced circuit features. You get a board that fits your needs.
Hybrid aluminum PCBs help you make smarter and better electronics. You can fix hard problems with heat and space. These boards help you build better products for today’s tech world.
Applications

Power Electronics
Power electronics are in devices that change or control electricity. These include power supplies, voltage regulators, and motor controllers. These circuits can get hot very fast. If you do not cool them, your device might stop working or not work well. Aluminum PCBs help with this problem. The metal base takes heat away from the power parts. This keeps your device working longer and more safely.
Many engineers pick aluminum PCBs for power electronics. They are good for high currents and voltages. You see them in solar inverters, battery chargers, and big power modules. The strong base holds heavy parts and does not bend easily. You can use these boards in hard places like factories or outside.
Tip: When you make power electronics, use a board that cools fast. This keeps your circuits safe and helps your device last longer.
LED Lighting
LED lights need to stay cool to work well. Bright LEDs make a lot of heat. If you do not move this heat away, the LEDs can get dim or break. Aluminum PCBs help keep LEDs cool. The metal base spreads heat out and away from the LEDs.
You find aluminum PCBs in street lights, car headlights, and screens. These boards let you put more LEDs in a small space. You get bright lights that last a long time. The solder mask keeps the copper safe and makes the board look nice. You can pick a white solder mask to reflect more light and help cooling.
Here is a table that shows how aluminum PCBs help in different ways:
Application Area | Benefit of Aluminum PCBs |
|---|---|
LED Lighting | Moves heat from bright LEDs, so they last longer. |
Automotive Electronics | Helps electric car batteries handle heat over 100 W. |
Renewable Energy | Used in solar inverters to cool power circuits. |
Industrial Automation | Makes boards strong in hot places. |
Note: If you want your LED lights to be bright and last, use aluminum PCBs. They cool better and do not fail as much.
Automotive
Aluminum PCBs are in many car electronics. Modern cars have more sensors, lights, and control units. These parts need boards that can handle heat, shaking, and bumps. Aluminum PCBs give you the cooling and strength you need.
Electric cars use aluminum PCBs in battery systems. These boards handle heat over 100 watts. The metal base keeps the board cool and safe. You also see aluminum PCBs in headlights, brake lights, and dashboards. The board does not bend or break from bumps or shaking.
Your car electronics work well and do not crack when it gets hot or cold. You can trust your car to work in summer and winter.
Tip: For car electronics, use a board that stays cool and strong. Aluminum PCBs help your car run safely and well.
Industrial Equipment
You find aluminum PCBs in lots of factory machines. These boards help machines work well and last longer. Machines in factories run for many hours each day. They can get very hot if used for a long time. If heat is not controlled, machines might stop or break.
Aluminum PCBs help control heat in machines. The metal base moves heat away from power parts. This keeps machines safe and working well. You see aluminum PCBs in motor controllers and power converters. They are also in automation systems. These boards stop machines from getting too hot and failing.
Many machines use high-power electronics. For example, you find aluminum PCBs in:
Robotic arms
Conveyor belts
Power supplies for factories
Welding machines
Lights used in factories
These machines need strong circuit boards. Aluminum PCBs do not break from shaking or bumps. The metal base keeps the board flat and tough. You do not have to worry about cracks or broken lines. Your machines keep working, even in hard places.
Tip: To make your machines last longer and stop less, pick aluminum PCBs for your control boards.
Aluminum PCBs also make machines safer. The boards can handle high currents and voltages. The dielectric layer keeps copper and metal apart. This stops short circuits and keeps workers safe.
Here is a table that shows how aluminum PCBs help machines:
Feature | Benefit for Industrial Equipment |
|---|---|
High thermal conductivity | Stops power parts from overheating |
Strong mechanical base | Does not break from shaking |
Good electrical insulation | Stops short circuits |
Long lifespan | Saves money on repairs |
You can make smaller and lighter control boards with aluminum PCBs. These boards let you put more parts in a small space. You do not have to worry about heat building up. This saves space in machines and control boxes.
Aluminum PCBs also help meet safety rules. Many factories need machines that work in hot or dirty places. The solder mask keeps copper safe from dust and water. The silkscreen gives clear labels for easy fixing.
If you want machines that work well and are safe, use aluminum PCBs. You get better results, less stopping, and save money. Your machines will work better for you!
Manufacturing
Material Prep
Making an aluminum PCB starts with getting the right materials ready. You need three main layers for the board. These are copper foil, a thermally conductive dielectric, and an aluminum base. Each layer is important for how the board works.
Copper Foil: You pick how thick the copper is by how much current your circuit needs. Thicker copper can carry more power and helps move heat away.
Dielectric Layer: This layer goes between the copper and the aluminum. It must move heat well and stop electricity from leaking. Most makers use a special resin or polymer here.
Aluminum Base: You pick the aluminum base because it is strong and moves heat away from hot spots. The base often has a cover to stop scratches and rust.
You must keep all the materials clean and free from dirt or oil. Any dust can cause problems later in the process. You also need to cut the aluminum base to the right size for your board. This step helps make a strong and reliable PCB.
Tip: Always check your aluminum base and copper foil for good quality. Good materials help your board last longer and handle heat better.
Pattern Transfer
Pattern transfer puts your circuit design onto the copper layer. This step makes the paths for electricity on your board.
Apply Photoresist: You cover the copper with a film that reacts to light.
Expose to UV Light: You put a mask with your circuit pattern over the board. UV light shines through the mask and hardens the film where you want copper to stay.
Develop the Pattern: You wash the board to remove the soft film. Only the parts with your design stay safe.
Next, you remove the extra copper. The protected parts become the traces and pads for your parts. You must be careful in this step. If you leave too much copper, you get shorts. If you take away too much, your traces can break.
Note: Aluminum PCBs need special care in pattern transfer. The aluminum base can reflect light, so you must use the right settings.
Lamination & Curing
Lamination sticks all the layers together. You stack the copper, dielectric, and aluminum base in the right order. Then, you use heat and pressure to press them into one board.
The dielectric melts a little and fills any spaces.
The copper and aluminum stick tightly to the dielectric.
The whole stack cools and becomes a strong, flat board.
Curing makes sure the dielectric is set all the way. You heat the board to a certain temperature for a set time. This step locks in the heat and electrical features you need.
You must not let air bubbles or gaps form during lamination. These problems can hurt how the board handles heat and may cause it to fail later. Good lamination gives you a board that can handle heat and stress.
Tip: Always check your boards after lamination. Look for bends, bubbles, or weak spots. A well-laminated aluminum PCB works better and lasts longer.
Drilling & Metallization
Drilling and metallization are important steps when making aluminum PCBs. You need holes for putting in parts and linking layers. These steps help your board work well and last longer.
Drilling Process
First, you drill holes through the PCB layers. The holes let you add parts and make connections. Aluminum PCBs need special care when drilling. The metal base is harder than other PCB materials. You must use sharp drill bits and go at the right speed. If you drill too fast, you might hurt the copper or make rough edges.
There are two main types of holes in aluminum PCBs:
Through-holes go all the way through the board. You use them for big parts like connectors.
Resin-insulated holes have resin inside. The resin keeps the hole from touching the aluminum base. This stops shorts and keeps your board safe.
Tip: Always check the size and spot of each hole before drilling. Good holes help your board work better.
Metallization Process
After drilling, you add metal inside the holes. This step is called metallization. You coat the hole walls with copper. Metallization links the top copper layer to the bottom or other layers. You get strong paths for signals and power.
The metallization process has three main steps:
Cleaning: You clean the holes to remove dust and oil.
Activation: You treat the hole walls with chemicals so copper sticks.
Electroplating: You use electricity to put copper inside the holes.
Aluminum PCBs need extra care during metallization. Resin-insulated holes must stay covered. If copper touches the aluminum base, you can get shorts. You must check every hole for good copper and no gaps.
Here is a table that shows how standard and resin-insulated holes are different:
Hole Type | Used In | Insulation Needed | Metallization Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
Standard Through-hole | FR-4, simple PCBs | No | Easy copper plating |
Resin-insulated | Aluminum PCBs | Yes | Careful resin application |
Why Drilling & Metallization Matter
You need careful drilling and good metallization for a strong aluminum PCB. These steps help your board handle heat, power, and shaking. If you skip careful work, your board might break early.
Note: Good drilling and metallization make your aluminum PCB safer and work better. Always pick skilled makers for the best boards.
Comparison
Aluminum PCBs vs FR-4
FR-4 PCBs are in lots of electronics. FR-4 uses fiberglass and epoxy. These boards are good for low-power jobs. Aluminum PCBs have a metal base. The metal base moves heat away much faster. This means better cooling and stronger boards.
FR-4 boards can get hot and bend. Aluminum PCBs stay flat and strong when hot. You can use aluminum PCBs in places with lots of shaking or heat. FR-4 boards cost less for simple jobs. Aluminum PCBs cost more but last longer in tough places.
Here is a table that shows the main differences:
Feature | Aluminum PCBs | FR-4 PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Base Material | Aluminum | Fiberglass/Epoxy |
Thermal Conductivity | High | Low |
Mechanical Strength | Strong | Moderate |
Cost | Medium | Low |
Best Use | High-power, hot spots | General electronics |
Tip: For power electronics or LED lights, pick aluminum PCBs. They control heat better and last longer.
Aluminum PCBs vs Copper-Based
Copper-based PCBs use copper for the base. These boards handle heat and electricity very well. They work best for high temperatures and fast circuits. Aluminum PCBs cool well for medium heat and cost less.
Aluminum PCBs save money and are lighter. Copper-based PCBs are heavier and cost more. Use copper-based PCBs for the best performance. Aluminum PCBs are good for cheaper projects and many power electronics.
Here is a table that compares these two types:
Feature | Aluminum PCBs | Copper PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Cost | More expensive | |
Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
Thermal Management | Good for moderate temperatures | Superior for high temperatures |
Electrical Performance | Adequate for many applications | Superior, better for high-performance |
Aluminum PCBs help you save money and make lighter devices.
Copper PCBs give you better performance for very hard jobs.
Note: Pick copper-based PCBs for top electrical and heat control. Use aluminum PCBs for most power and lighting jobs.
Aluminum PCBs vs Ceramic
Ceramic PCBs use special materials like alumina or aluminum nitride. These boards handle very high heat and insulate electricity well. You find ceramic PCBs in aerospace, medical, and military devices. Aluminum PCBs control heat well and cost less.
Ceramic PCBs resist chemicals and work in tough places. They cost much more than aluminum PCBs. Use ceramic PCBs for the hardest jobs. Aluminum PCBs work well for most power and lighting needs.
Here is a table that compares all three types:
Feature | Aluminum PCBs | Copper-Based PCBs | Ceramic PCBs |
|---|---|---|---|
Cost | Medium | High | Very High |
Weight | Light | Heavy | Light |
Thermal Conductivity | High | Very High | Highest |
Electrical Insulation | Good | Good | Excellent |
Best Use | Power, LEDs | High-performance | Extreme environments |
Tip: Pick ceramic PCBs for extreme heat and chemicals. Use aluminum PCBs for most jobs that need good cooling and strong boards.
Selection Tips
Picking the right PCB helps your project work well. You need to choose a board that fits your needs. Here are some easy tips for picking the best aluminum PCB.
1. Know Your Thermal Needs
Think about how much heat your circuit makes. Aluminum PCBs are great for moving heat away fast. If your board gets hot, like in LED lights or power electronics, use aluminum PCBs. They keep your parts cool and help them last longer.
Tip: Pick aluminum PCBs if your board gets hot or if regular boards have heat problems.
2. Check Your Budget
Aluminum PCBs cost more than FR-4 boards. They cost less than copper or ceramic PCBs. If you want good cooling and strength but need to save money, pick aluminum PCBs. For simple jobs, FR-4 might be enough. For very hot or special jobs, you may need copper or ceramic.
3. Think About Board Structure
You can pick single-layer, double-layer, or multilayer aluminum PCBs. Single-layer boards are good for easy circuits. Double-layer and multilayer boards hold more parts and do harder jobs. Flexible and hybrid aluminum PCBs are good for special shapes or mixed features.
Board Type | Best Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Single-layer | LED strips, power modules | Simple, low cost |
Double-layer | Automotive, controls | More connections |
Multilayer | Telecom, medical, power | Complex, high power |
Flexible/Hybrid | Wearables, custom shapes | Bends, custom design |
4. Consider Mechanical Strength
If your device shakes, gets bumped, or is outside, use aluminum PCBs. The metal base keeps the board flat and strong. You get better results in cars, factories, or outdoor lights.
5. Look at Electrical Performance
Aluminum PCBs are good for high current and power. If you need fast signals or high voltage, check the copper thickness and dielectric layer. Thicker copper and a thin dielectric help with power and heat.
6. Review Your Application
Pick a PCB that matches your job. For LED lights, use a white solder mask to reflect more light. For power supplies, focus on cooling and strong connections. For cars or factory gear, pick boards with extra protection.
Note: Always talk to your PCB maker about what you need. They can help you choose the right materials and board type for your aluminum PCB.
If you follow these tips, you will pick the best aluminum PCB for your project. Your devices will work better, last longer, and have fewer heat or damage problems. Good PCB choices help your projects succeed every time.
Design Tips
Mounting & Holes
You need to plan your mounting and holes carefully when designing an aluminum PCB. The metal base makes drilling different from standard boards. You must use resin-insulated holes to prevent electrical shorts. These holes keep your components safe and your board reliable.
When you place mounting holes, think about where you will attach the PCB. Put holes near the edges for strong support. Use standard sizes for screws and standoffs. This helps you fit the board into cases or frames easily.
Here are some tips for mounting and holes in aluminum PCBs:
Use resin-insulated through-holes for component leads.
Space mounting holes evenly to avoid bending the board.
Avoid placing holes too close to copper traces.
Check the size and location of each hole before manufacturing.
Tip: Always mark your mounting holes clearly in your PCB design files. This helps the manufacturer drill them in the right place.
A good mounting plan keeps your aluminum PCB strong and safe. You reduce the risk of cracks and shorts.
Thermal Path
You must create a clear thermal path in your aluminum PCB design. The thermal path moves heat away from hot components. If you do not plan this path, your board can overheat.
Start by placing heat-generating parts close to the aluminum base. Use wide copper traces to help move heat. Keep the thermal path short and direct. This helps your board cool down faster.
Here is a simple checklist for thermal path design:
Place power components near the aluminum base.
Use thick copper for better heat transfer.
Connect hot spots to large copper areas.
Avoid blocking the thermal path with other parts.
Thermal Path Feature | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
Wide copper traces | Moves heat quickly |
Short path length | Reduces heat buildup |
Direct connection | Improves cooling efficiency |
Note: Good thermal management in aluminum PCBs helps your devices last longer and work better.
You can use thermal vias to connect the top copper layer to the aluminum base. These vias give heat more ways to escape. Always check your thermal path during design reviews.
Routing & Grounding
You need smart routing and grounding for a strong aluminum PCB. Routing means how you lay out the copper traces. Grounding keeps your signals safe from noise.
Keep your traces short and wide for power lines. This lowers resistance and helps with heat. Do not cross traces over mounting holes or sharp edges. This prevents damage during assembly.
For grounding, use a solid ground plane if possible. Connect all ground points to this plane. This reduces electrical noise and improves safety.
Here are some best practices for routing and grounding:
Use wide traces for high-current paths.
Keep signal traces away from power traces.
Place ground vias near sensitive components.
Avoid sharp turns in traces to reduce stress.
Routing & Grounding Tip | Benefit for Aluminum PCBs |
|---|---|
Solid ground plane | Lowers noise, boosts safety |
Wide power traces | Handles more current, less heat |
Ground vias | Improves signal stability |
Tip: Review your routing and grounding before sending your design to the manufacturer. Good layout helps your aluminum PCB work better in real-world conditions.
You get better performance and reliability when you follow these design tips for aluminum PCBs.
Dielectric Thickness
Dielectric thickness is important for how your aluminum PCB works. It affects how the board handles heat and electricity. You need to pick the right thickness for your project. The dielectric layer sits between the copper and the aluminum base. This layer keeps the copper and metal apart. It also helps move heat away from hot spots.
If you use a thin dielectric layer, heat leaves the copper faster. This helps your board cool down quickly. Thin layers also make it easier for heat to move. Devices like LED lights or power supplies work better with less heat.
A thick dielectric layer gives more electrical insulation. This means your board can handle higher voltages safely. You might need a thicker layer for high voltage or extra safety. But thick layers slow down how fast heat moves. Your board may get hotter if the dielectric is too thick.
You need to balance heat movement and electrical safety. Here is a table to show the differences:
Dielectric Thickness | Thermal Conductivity | Electrical Insulation | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
Thin (50-100μm) | High | Moderate | High-power, LED, power supply |
Medium (100-150μm) | Good | Good | General electronics |
Thick (150-200μm) | Moderate | High | High-voltage, safety circuits |
Tip: For most aluminum PCBs, pick a dielectric thickness between 75μm and 150μm. This gives you good cooling and safety.
When you design your aluminum PCB, check the dielectric specs. Look for high thermal conductivity and the right voltage rating. Ask your PCB maker for help if you are not sure.
Choosing the right dielectric thickness helps your PCB work better. Your board will last longer and handle tough jobs. Always match the thickness to what your project needs. This helps stop overheating and keeps your circuits safe.
Aluminum PCBs help control heat, last a long time, and are very strong. They work best in things like power electronics, LED lights, and car systems. If you need a good PCB maker, Philifast has advanced aluminum PCB options and checks quality carefully. Before picking a board, think about your design and ask experts for advice. For more help, look at technical guides or ask Philifast for answers.
Tip: Use aluminum PCBs if your project needs great heat control and to last a long time.
FAQ
What is an aluminum PCB?
An aluminum PCB is a printed circuit board with an aluminum base. You use it when you need better heat control. This kind of PCB works well for high-power jobs and LED lights.
Why should you choose aluminum PCBs for LED lighting?
Aluminum PCBs help keep LED lights cool. They move heat away from the LEDs fast. This keeps your lights bright and helps them last longer.
Can you cut or shape aluminum PCBs easily?
You can cut or shape aluminum PCBs, but you need special tools. The metal base is harder than regular boards. Always ask your PCB maker for the best way to do it.
How does the dielectric layer affect thermal management?
The dielectric layer sits between the copper and aluminum. If the layer is thin and good quality, heat moves faster to the aluminum base. This helps your parts stay cool and work better.
Are aluminum PCBs more expensive than FR-4 PCBs?
Aluminum PCBs usually cost more than FR-4 PCBs. You pay extra for better heat control and stronger boards. For high-power or outdoor devices, the extra cost means better performance.
What applications use aluminum PCBs the most?
You find aluminum PCBs in LED lights, power supplies, car electronics, and factory machines. These boards work best when you need strong heat control and reliability.
Can you use aluminum PCBs for multilayer designs?
Yes, you can use aluminum PCBs for multilayer designs. These boards support complex circuits and high power. You get better cooling and strong support for your parts.
How do you prevent short circuits in aluminum PCBs?
You stop short circuits by using resin-insulated holes and a good dielectric layer. Always check your design to make sure copper and aluminum are kept apart.


